Fibromyalgia treatment- not easy, but possible!
How is fibromyalgia treated?
There is no cure for fibromyalgia. However, symptoms can be treated with lifestyle changes and medications. Fibromyalgia can be a chronic condition and as such sometimes difficult to treat. There is no magic bullet for fibromyalgia treatment. Much of the success in treatment depends on your motivation and persistence.
Let’s divide treatment options into non-pharmacological (ie no drugs) and pharmacological therapies.
Non-pharmacological treatment
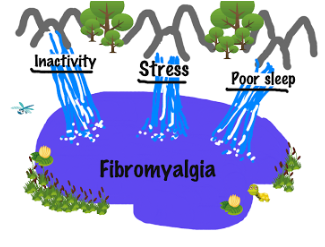
I think this is the most important aspect of fibromyalgia treatment. Since we know that stress, poor sleep, and physical inactivity exacerbate fibromyalgia, no fibromyalgia treatment is complete without addressing all of these issues. Think of fibromyalgia as a lake, where each of these factors is a stream feeding into the lake. To dry up the lake, we must first take care of these streams.
1. Improve your sleep
Refreshing sleep is helpful in reducing the pain of fibromyalgia. If you snore, you may have sleep apnea interrupting your sleep even if you don’t realize it. Restless leg syndrome is not uncommon in people with fibromyalgia. Having a sleep study may help diagnose these problems. If pain wakes you up at night, you can try Tylenol-PM before going to bed (if there are no contraindications). Everyone, including people with fibromyalgia, needs good sleep hygiene. These are some important steps for good sleep hygiene:
- Have a regular bed-time
- Stop drinking caffeine at least 6 hours before going to bed
- Lighten up dinner, and avoid eating 3 hours before bed time
- Avoid vigorous physical activity or exercise close to your bed time
- Make your bedroom a sanctuary for sleep. This means taking out EVERYTHING that is not related to sleep- including your TV. Your bed is your place for sleeping, not for talking on the phone, eating, watching TV, or talking on the phone.
- Turn your clock away from you. If you cannot sleep, DO NOT check out the time!
- Avoid taking naps during the day. This just makes you not be tired at night.
2. Exercise!
Many people with fibromyalgia have a hard time exercising because of the pain. Other reasons for lack of exercise may include long work hours, busy family life, fatigue after a long day, etc. However, exercise is one of the best treatments for fibromyalgia. Exercise helps tone and condition your muscles. In addition, it increases the levels of natural chemicals in the body that reduce pain and fatigue. People with fibromyalgia will need to start exercise lightly and build slowly over time. Expect some discomfort initially, but not pain. Most people with fibromyalgia find exercises in the water most tolerable, because water cushions the impact. Water-aerobics and Aquatherapy are excellent ways to start. Stretching and yoga are also very helpful. Other low-impact exercises include walking, biking, and Pilates. The goal is to exercise at least 30 minutes, 3 times per week.
3. Reduce your stress
Relaxation techniques, Yoga and Tai-Chi may be very helpful in stress reduction and can significantly improve symptoms of fibromyalgia. Biofeedback and cognitive behavioral therapy are also two evidence-based modalities that have been successful in improvement of fibromyalgia symptoms. In biofeedback, persons with fibromyalgia gain awareness of their typically unconscious bodily responses to stress, such as breathing and heart rate, and learn to modify these responses to physical and emotional stress. The goal of cognitive behavioral therapy is to change the way a person thinks about (cognitive) and responds to (behavioral) their disease.
4. Other therapies…
- Acupuncture
- Some studies have shown benefits of acupuncture in treatment of fibromyalgia pain.
Pharmacological treatment
Medications used in fibromyalgia:
- Anticonvulsants: Gabapentin (Neurontin) and Pregabalin (Lyrica)
It is thought that these medications reduce pain by blocking certain chemicals that increase pain transmission.
- Serotonin/Norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors: Duloxetine (Cymbalta) and Milnacipran (Savella)
These medications block the re-uptake of both serotonin and norepinephrine by nerve cell endings and can help with pain and fatigue.
- Tricyclic antidepressants: Amitriptyline (Elavil), Nortriptyline (Pamelor)
The most common side effects are dry mouth and grogginess.
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs): Fluoxetine (Prozac), Paroxetine (Paxil), others
These are antidepressants that work by increasing serotonin levels in the brain and have been helpful in fibromyalgia.
- Muscle relaxant: Cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril), Carisoprodol (Soma)
Usually used in combination, these drugs can help relieve muscle tension.
- Other medications:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Ibufprofen, Meloxicam, etc.
Topical analgesic creams and patches: Capsacin, Aspercreme, Voltaren gel, Flector patch, etc.
Analgesics: Tramadol (Ultram)
Opioids/narcotics: I usually do not recommend these medications for a chronic pain condition like fibromyalgia.
Also read:
What is fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia- diagnosis
Reference:
American College of Rheumatology http://www.rheumatology.org/practice/clinical/patients/diseases_and_conditions/fibromyalgia.asp
Arthritis foundation http://www.arthritis.org/
F Wolfe, DJ Clauw, MA Fitzcharles, DL Goldenberg, RS Katz, P Mease, AS Russell, J Russell, JB Winfield, MB Yunus. The American College of Rheumatology Preliminary Diagnostic Criteria for Fibromyalgia and Measurement of Symptom Severity. Arthritis Care & Research,Vol. 62, No. 5, May 2010, pp 600–61






