What are some of the rheumatoid arthritis symptoms?
Rheumatoid arthritis symptoms can range from mild to moderate to severe. Although joint pain and swelling is the hallmark of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), other organs may also be affected.
Constitutional symptoms
People with RA may note fever, fatigue, body aches, and weight loss
Joints
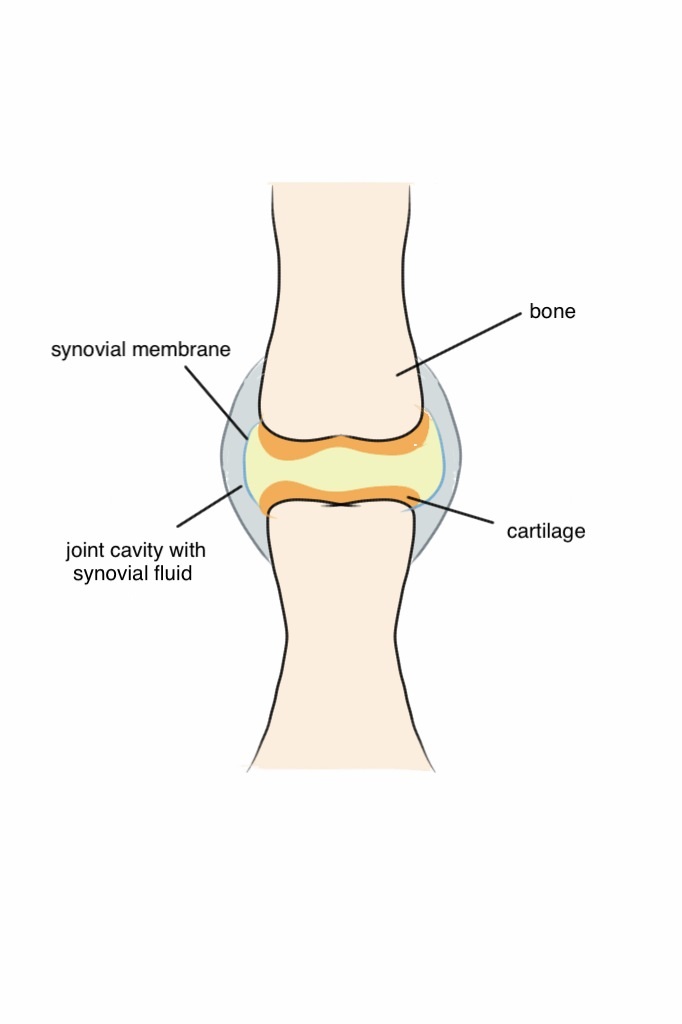
Rheumatoid arthritis affects the synovial joints. These are joints that are lined by a synovial membrane. The most commonly affected joints are the small joints of the hands and feet, but RA can also be seen in the shoulders, elbows, hips, knees, and cervical spine. Less commonly temporomandibular joints (TMJ) and sternoclavicular joints may be affected.
Inflammation of the synovial membrane causes pain, swelling, redness and warmth. The affected joints are usually stiff after extended periods of inactivity, especially after waking up in the morning. Synovial inflammation may eventually lead to erosion of the adjacent bone and lead to deformity.
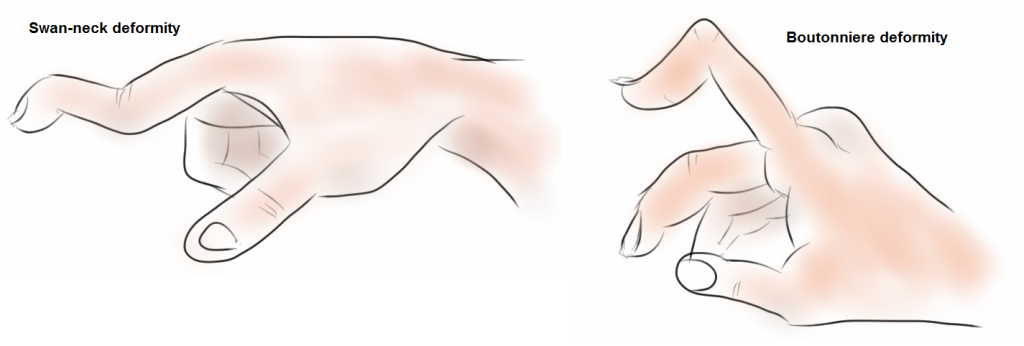
With longstanding untreated RA, joint deformity can occur. “Swan-neck deformity” refers to flexion of the hand joint distally and extension proximally, so the finger resembles neck of a swan. In Boutonniere deformity, the distal joints are extended and the middle joint is flexed. Fingers may also deviate laterally; a finding termed “ulnar deviation”. “Z-deformity” is caused by subluxation of the thumb at the base and hyperextention distally so the thumb appears like a Z.
The toes may turn upward, therefore putting more pressure on the bottom of the toes. People with RA sometimes describe this as if they are “walking on marbles”.
Extra-articular involvement in RA
Involvement of organs other than joints:
Skin
Rheumatoid nodules are painless lumps under the skin that develop in pressured areas like under the forearm, on the elbow, and on the tendons of the hands, among other areas.
Heart
RA can cause inflammation of the lining of the heart (pericarditis). This causes a sharp chest pain worse when taking a deep breath, and in severe cases can collapse the chambers of the heart.
People with RA are more prone to developing atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) and heart attacks.
Lungs
Similar to pericarditis, inflammation of the lining of the lungs (pleuritis) can cause chest pain and difficulty breathing. Rheumatoid arthritis can also cause inflammation of the lung tissue leading to interstitial lung disease. Occasionally patients with RA can have nodules (similar to rheumatoid nodules) in the lungs.
Kidneys
Chronic inflammation from severe, untreated RA can lead to deposits of inflammatory protein (amyloid) in the kidneys. Amyloidosis is the main cause of kidney failure in RA.
Blood
People with rheumatoid arthritis may be anemic. The anemia can be caused by chronic inflammation (anemia of chronic disease) or destruction of the red cells by the immune system. An enlarged spleen, which may be a late complication of rheumatoid arthritis, can cause low white blood cells (Felty’s syndrome).
Blood vessels
Inflammation of the blood vessels can cause a variety of symptoms, some that may be life threatening.
Nerves
Inflammation in the wrist can put pressure on the median nerve and cause carpal tunnel syndrome. A similar process in the ankle can cause numbness and tingling in the feet.
Erosion of the odontoid process (the part of the spine in the neck where the skull rests on) can cause instability in the neck. Slipping of the unstable vertebrae can compress the spinal cord and eventually lead to quadriplegia.
Eyes
Inflammation of the white part of the eye can cause pain and changes in the vision.
Some people with rheumatoid arthritis develop dry eyes and dry mouth- a syndrome called Sjogren’s syndrome which may also be seen with a variety of other autoimmune diseases.
Bones
Rheumatoid arthritis, as well as some of the medications used to treat it, can increase the risk for osteoporosis.
Lymph
Although uncommon, lymphoma risk is increased in people with RA.
See also:
Rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis
Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Reference:
- http://www.arthritis.org/conditions-treatments/disease-center/rheumatoid-arthritis/
- http://www.rheumatology.org/practice/clinical/patients/diseases_and_conditions/ra.asp
- http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/rheumatoid-arthritis/DS00020
- http://www.uptodate.com/contents/rheumatoid-arthritis-treatment-beyond-the-basics?detectedLanguage=en&source=search_result&search=rheumatoid+arthritis+patient&selectedTitle=1%7E150&provider=noProvider






